Urticaria



Urticaria
Acute Urticaria is said to affect 10 to 20 % of population at sometime during life, it is most common in young adults. It is also known as hives, are an outbreak of swollen, pale, red, bumps, patches on the skin that appear suddenly-either as a result of allergies or for other reasons.
Episodes of Urticaria occurring at least twice a week for six weeks are considered to be chronic.
Acute Urticaria is defined as persisting for less as 6 weeks where as chronic Urticaria refers to episodes lasting more than 6 months.
Angioedema is similar to hives, but the swelling occurs beneath the skin instead of on the surface. Angioedema is characterized by deep swelling around the eyes, lips and sometimes of genitals, hands and feet.
Swelling generally last longer usually go away in 24 hours
Types of Urticaria
Nonimmunologic
1
Physical Urticarias
dermographism ,adrenergic, pressure,viabatory,solar,
cholinergic,local heat, cold
2
Infections
3
Neoplasm
4
Recurrent idiopathic

5
Hereditary Urticaria
6
Vasculitis
7
Anaphylaxis
8
Exercise induced

1
Food
2
Autoimmune anti IgE and/or antiFcERi
3
Transfusion reaction
4
Acquired C1 INH deficiency

5
Drugs
6
Insect sting
7
Schnitzier syndrome
8
Exercise induced

What cause hives?
In majority of cases it’s difficult to find a cause.
More than 40 % of cases autoimmunity plays a role
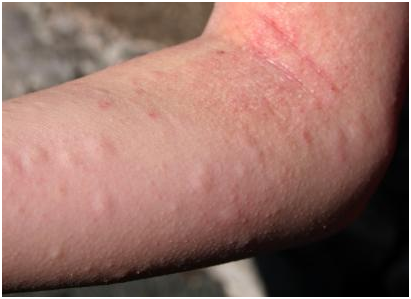


What are the Symptoms of Urticaria?
Itching is invariable .it is pricking or burning in quality, worse in the evening or night time. Relieved by rubbing than scratching.50 % of patients also have angioedema And wheals it can occur anywhere on the skin for example scalp, sole and palms.
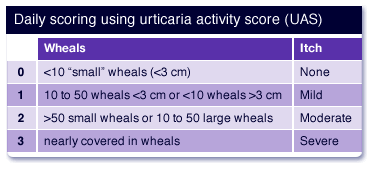
Urticaria score
It is done for every patient to assess the severity of the disease.
The clinical details noted were a personal or family history of atopy and the duration in months since the onset of Urticaria.
The number and size of the wheals, severity of itching and extent of body involvement were scored as follows:
Number of wheals no wheals=0, 1-5=1, 6-15=2, 16-25=3, > 25 =4
Wheal size, none=0, 2 cm=3, > 4 cm=4
Itching none=0, mild=1, moderate=2, severe=3, very severe=4
Extent of body involvement none=0,1-10%=1, 11-30%=2, 31-50%=3, > 50%=4
Associated systemic symptoms and angioedema were also re- corded.
What are the Aggravating factors?
IgE mediated food allergy
Idiosyncratic reactions to food additives
Aspirin and viral infection may exacerbate but never causative.
Investigation
Your doctor may advise you battery of investigations based on your symptoms and physical examination
1
Allergy Testing
2
Urine analysis
3
ESR
4
ASST
5
Thyroid antibodie

6
Allergy Testing
7
Metabolic screen
8
ANA
9
APST
10
Others

All patients should discontinue short acting antihistamines for at least three days and long acting antihistamine for at least seven days before skin tests were performed.
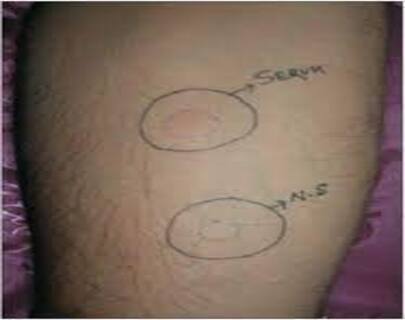


How is ASST test performed?
Asst test is performed by your doctor in the clinic; patient’s venous blood was placed in sterile plastic Autologous_Serum_Skin_Test-250x359tubes and allowed to clot at room temperature for 30 minutes. Then the serum was separated by centrifugation at 500 x g for 15 minutes and kept in aliquots for use in the ASST. Sample (50 µl) of autologous serum and 0.9% sterile saline (for negative control) were separately injected intradermally into the volar aspect of the patient’s forearm skin with 27G needle, leaving gaps of at least three centimetres. A skin prick test with histamine (10 µg/µl) was used as a positive control. Areas known to have been involved in spontaneous wheals in the last 24 hours were avoided. Skin prick tests with histamine were interpreted after 15 minutes. Wheals and flare responses were measured after 30 minutes. A positive ASST was defined as a serum-induced wheal which was both red and had a diameter of 1.5 mm or more than the saline-induced response at 30 minutes