Anaphylaxis



Anaphylaxis is serious, potentially life threatening allergic reaction. It can occur within seconds or minutes of exposure to something you’re allergic to, such as insect bites, foods, and medications.
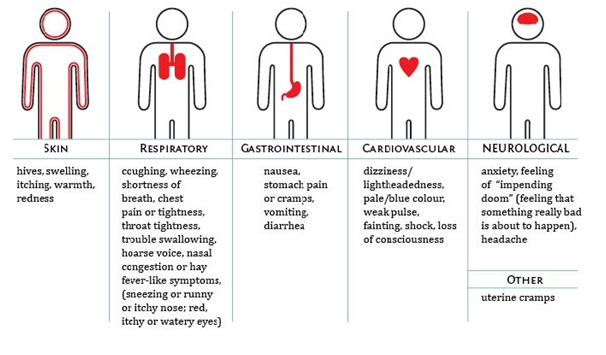
Symptoms
generalised flushing of the skin
nettle rash (hives) anywhere on the body
sense of impending doom
swelling of throat and mouth
difficulty in swallowing or speaking
alterations in heart rate
severe asthma
abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting
sudden feeling of weakness (drop in blood pressure)
collapse and unconsciousness
What can cause Anaphylaxis?
Common causes include
Foods
such as peanuts, tree nuts (e.g. almonds, walnuts, cashews, and Brazil nuts), sesame, fish, shellfish, dairy products and eggs.
Insect bites
Non-food causes include wasp or bee stings, natural latex (rubber), penicillin or any other drug or injection.
Medications
both over the counter and prescribed, can cause life threatening allergic reactions. Individuals can also have anaphylactic reactions to herbal or ‘alternative’ medicines.
Others
some people, exercise can trigger a severe reaction – either on its own or in combination with other factors such as food or drugs (e.g. aspirin).
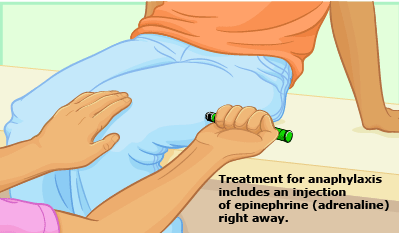



How to manage and treat Anaphylaxis?
After recognizing the signs of anaphylaxis patient should be kept in head low position and adrenaline should be injected intramuscularly as soon as possible.
Adrenaline auto-injectors are prescribed for those believed to be at risk. Adrenaline (also known as epinephrine) acts quickly to constrict blood vessels, relax smooth muscles in the lungs to improve breathing, stimulate the heartbeat and help to stop swelling around the face and lips.
Children and caregivers need to be educated on how to avoid allergens and/or other triggers. However, because accidental exposure is a reality, children and caregivers need to be able to recognise symptoms of an anaphylaxis and be prepared to administer adrenaline according to the individual’s Action.
om Anaphylaxis?
If a patient has suffered a bad allergic reaction in the past – whatever the cause – then any future reaction is also likely to be severe. If a significant reaction to a tiny dose occurs, or a reaction has occurred on skin contact, this might also be a sign that a larger dose may trigger a severe reaction. It is particularly important that those with asthma as well as allergies are seen by an allergy specialist because asthma can put a patient in a higher risk category. Where foods such as nuts, seeds, shellfish and fish are concerned, even mild symptoms should not be ignored because future reactions may be severe.