Asthma




Overview
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of airways, in which airways become narrow and swell and produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing, wheezing and shortness of breath.
Underdiagnosis of asthma is a significant issue that can lead to untreated asthma and potential harm to patients. Studies indicate that a considerable portion of individuals with asthma in the community remain undiagnosed, ranging from 20% to 70%.
Symptoms
1

Recurrent episodes of wheezing,cough and Shortness of Breath
2

Chest tightness or pain
3

Waking up at night due to Asthma symptoms
4

Cough, wheezing, chest tightness after exposure to airborne allergens or pollutant,and after exercise
5

Common Cold that goes to the chest and takes weeks to clear


Asthma Triggers

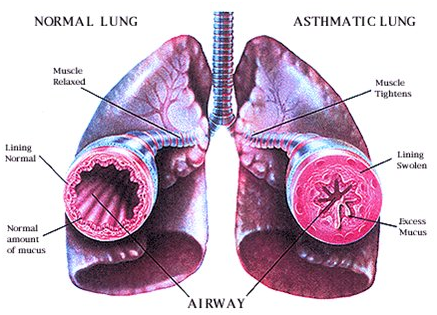
What happens to lung during an asthma attack?
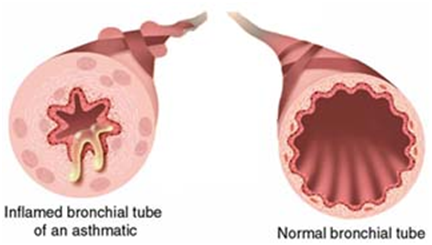
On exposure to Asthma triggers, airway mucous (inner lining of the airway) swells up and secretes thick mucus, which obstructs the airways. The muscles around the airway tighten making the airway narrower. All this makes breathing very difficult.
If the doctor suspects asthma how will he confirm the diagnosis?
1

Detailed evaluation of symptoms
2

Routine tests for example x-ray chest, blood test etc

3

Physical examination
4

Pulmonary function testing

5

Allergy testing- This test is done to distinguish allergic asthma from nonallergic asthma.
Lung function tests are done to
- Determine the cause of breathing problems.
- Diagnose certain lung diseases, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Evaluate a person’s lung function before surgery.
- Check the lung function of a person who is regularly exposed to substances such as asbestos that can damage the lungs.
- Check the effectiveness of treatment for lung diseases

The tests determine how much air your lungs can hold, how quickly you can move air in and out of your lungs
This test is recommended in suspected and diagnosed asthma patients, Smokers and people who are exposed to chemical fumes, pollution, and respiratory irritants.
What are the medications used for treatment of asthma and how they work?
Asthma treatment aims to control and manage symptoms, reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, and improve daily functioning and quality of life. The treatment approach may vary depending on the severity of the asthma.
Asthma treatment aims to control and manage symptoms, reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, and improve daily functioning and quality of life. There are two main types of medications used in asthma treatment
1.Quick-Relief Medications:
These medications provide immediate relief by relaxing the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe.
2.Controller medications:
To reduce inflammation and swelling in the airways over time to prevent symptoms and asthma attacks. It includes inhaled corticosteroids and combination inhalers ( with both a corticosteroid and a long-acting bronchodilator). These inhalers must be taken daily, even when feeling well, to be effective.
So preventer medications should be taken regularly till the doctor advises it to be stopped.

What are Inhalers?
Inhaler is a Medical device that delivers medicine directly to the lungs. Inhalers allow medications to be delivered directly to the lungs, providing targeted treatment and reducing the systemic side effects compared to oral medications.
Proper technique is important for the effective use of inhalers. Spacer devices can be used with MDIs to improve delivery to the lungs.
Providers should demonstrate proper inhaler technique and regularly assess patient skills to ensure optimal medication delivery and asthma control.
What should I do to keep my Asthma under control?
1

Take the correct amount of medicine.
2

Avoid coming in contact with allergen.
3

Avoid asthma triggers.
4

Avoid emotional stressful situations.
5

Regular follow up with your physician.
Complications of Asthma
Complication of asthma includes respiratory failure, death and growth retardation in children.
Myths of Asthma
1

Asthma is a contagious disease.
2

Inhalers are addictive.
3

Steroid inhalers have a lot of side effects.

4

People with asthma cannot work or exercise.
5

Inhales are very strong and they should be used as last resort in asthma.

Realities of Asthma
1

Asthma is not a contagious disease.
2

Inhalers are not addictive.
3

Inhaled steroids are safe even if taken for a prolonged period.

4

Asthmatics on regular treatment can work and exercise normally.
5

Inhalers deliver a small dose of medicines so they are the fastest and safest form of treatment for asthma.

Types of Asthma
1

Allergic Asthma
2
Non allergic Asthma

3
Childhood asthma
4

Pregnancy induced asthma
5

Exercise induced Asthma

6
Steroid unresponive asthma
7

Obesity induced asthma
8

Aspirin induced asthma

9
Occupational asthma
10

Exacerbation prone asthma
11

Asthma in elderly

12
Factitious asthma
13

Asthma with irreversible airflow obstruction
14

Coexistent Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

15
Steroid dependent asthma

Why is your asthma not responding to inhalers?
Inhalational therapy is very effective in treating and controlling asthma symptoms but few patients fail to respond, and continue experiencing troublesome asthma related symptoms even on taking asthma medications on regular basis.
The reason behind unresponsiveness is commonly due to the wrong inhaler technique, tobacco smoke, significant environmental allergen exposure and significant occupational exposure.
Beside this some drugs for example beta blockers, NSAIDS, ACE inhibitors produces asthma like symptoms.
Any concurrent disease for example gastroesophageal reflux disease, COPD, chronic sinusitis, rhinitis, systemic disease, thyrotoxicosis and vasculitis may be the cause of poor symptom control.
Your physician needs to diagnose and treat the concurrent medical condition for the better control.
Role of biologics in Asthma control
Biologics have emerged as an important treatment option for asthma, especially for patients with severe asthma that is not well-controlled with standard therapies. These advanced therapies target specific components of the immune system involved in the inflammatory processes underlying asthma. Here’s an overview of their role in asthma control:
Benefits of Biologics in Asthma Management
- Targeted Therapy: Biologics specifically target underlying immune pathways contributing to asthma, leading to more precise treatment compared to broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Reduction in Exacerbations: Clinical trials and real-world studies have shown that biologics significantly reduce the frequency and severity of asthma exacerbations.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Better asthma control with biologics can lead to improved overall quality of life, with fewer symptoms and limitations on daily activities.
- Reduced Need for Oral Corticosteroids: Long-term use of oral corticosteroids can have significant side effects. Biologics help reduce or eliminate the need for these drugs in many patients.
Considerations and Challenges
- Cost: Biologics are expensive, which can limit access for some patients
- Long-Term Safety: While generally safe, long-term safety data are still being collected for some of these newer therapies.
- Administration: Most biologics are administered via injection or infusion, which might be less convenient than inhaled medications.
- Identification of Suitable Candidates: Not all asthma patients will benefit from biologics. Proper patient selection through biomarkers like blood eosinophil counts or IgE levels is crucial.