Services


Diagnostic services play a crucial role in the healthcare system by providing accurate and timely information necessary for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases. It is aramount to have a correct diagnosis done, identifying the root cause & eliminating the same, can itself give major relief in symptoms & can even cure the disease.
SKIN PRICK TEST/ALLERGY SKIN TEST
Skin prick Testing is an essential first step in patients suffering from Asthma, Food allergy,Allergic Rhinitis, Eczema/Atopic dermatitits, and insect allergy. It paves the way for the more targeted and effective treatment.Identifying the culprit allergen through allergy testing can be a game changer for those living with allergies
Allergic Rhinitis
Asthma
Food Allergy
Atopic dermatitis/Eczema
Insect Allergy
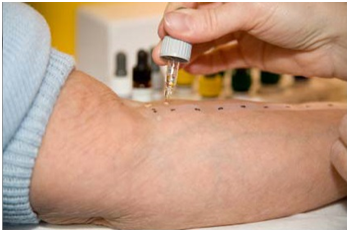


HOW SKIN PRICK TEST IS DONE?
1.Preparation : The test is performed on the forearm or back.The skin area is cleaned with alcohol to ensure it's free of any contaminantion.
2.Marking the Skin: Small marks are made on the skin to identify where each allergen will be applied.Each mark corresponds to a different allergen extract.
3.Application of Allergen Extracts: A drop of each allergen extract is placed next to its corresponding mark on the skin.The positive control and negative control are also applied.
4.Pricking the Skin: A sterile lancet is used to prick the skin through each drop of allergen extract.The prick should be shallow enough to avoid bleeding but deep enough to introduce the allergen to the skin.
5.Observation: The skin is observed for a reaction over a period of about 15 to 20 minutes.A positive reaction typically involves a raised, red, itchy bump (wheal) surrounded by a red area (flare).The size of the wheal and flare are measured and compared to the controls.
6.Interpretation of results: A wheal that is significantly larger than the negative control and comparable to or larger than the positive control indicates a positive reaction to the allergen.The size of the reaction helps in assessing the sensitivity to each allergen.
7.Aftercare: The tested area may be cleaned and Patients are advised to report any delayed reactions.
8.Precautions and Considerations: Skin prick testing should be performed by a trained healthcare professional.It is important to consider the patient's medical history and current medications, as some medications (e.g., antihistamines) can affect the test results.
SPT is generally safe but may not be suitable for individuals with certain skin conditions or severe allergies.
Prerequisites
The patient needs to avoid taking anti-histamines and certain other medications before the test. Long acting antihistamines (those that do not cause drowsiness) should be stopped for five days; short acting antihistamines can be stopped 76 hours beforehand.
Potential Risks of Non-Specialist Care
Misinterpretation of test results
Over diagnosis
Mismanagement
Over prescription of meds. and treatments
Costly and unnecessary allergen avoidance
ALLERGY BLOOD TESTS
Blood tests measure the amount of IgE antibody circulating in the blood.Commonly known as Immunocap ELISA or more mornden Component resolved diagnosis.Allergy blood tests are valuable tools in diagnosing allergies, especially in cases where skin testing is not feasible or safe .Blood tests are expensive and results take longer compared to skin prick testing.While blood tests are accurate, they may not be as sensitive as skin prick tests in detecting certain allergies.
The test is carried out on a small sample of blood,usually taken from a vein in the arm in the usual way, Sample is then sent to the laboratory. both false positive and false negative results are possible, and the presence of IgE in a test does not necessarily mean that the substance is actually causing the patient’s symptoms.



PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING / SPIROMETRY
Lung function tests are done to:
Early Diagnosis: Identifies lung diseases at an early stage, improving treatment outcomes.
Symptoms: Persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
Monitoring: Assessing the progression of lung diseases and the effectiveness of treatment.
Pre-Surgical Evaluation: Ensuring patients have adequate lung function before undergoing surgery.
Occupational Health: Evaluating the impact of exposure to environmental or occupational irritants.
The testing may take from 5 to 30 minutes, depending upon how many tests are done.
How the Test is performed?
How to Prepare for the Test?
- Do not eat a heavy meal before the test
- Do not smoke for 4 – 6 hours before the test
- you need to stop using bronchodilators or inhaler medications
- You may have to breathe in medication before or during the test.
How the Test Will Feel?
Since the test involves some forced breathing and rapid breathing, you may have some temporary shortness of breath or lightheadedness. You breathe through a tight-fitting mouthpiece, and you’ll have nose clips.
Medicines to avoid before PFT
Short acting Beta2 Agonists (Eg. Salbutamol, Levosalbutamol) - 6 hours
Long Acting Beta2 Agonists (Eg. Formoterol, Salmeterol)-12 hours
Long acting Antimuscarinic bronchodilators Tiotropium-24 hours
Long acting Theophyllines-48 hours
Short Acting Antimuscarinic bronchodilators .e.g. Ipratropium - 8 hours
Inhaled steroids- 1 hour:
Normal Results
A pulmonary function test (PFT) report is considered normal when the results fall within a certain range of values that are considered typical for a person’s age, sex, height, and other factors. Normal values can vary slightly depending on the specific equipment used and the population being tested, Normal results are expressed as a percentage. A value is usually considered abnormal if it is less than 80% of your predicted value.
It’s important to note that PFT results are just one piece of information used to assess lung health, and they should be interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings and the patient’s medical history.
Parameters measured in Pulmonary Function test
1

Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
2

Forced vital capacity (FVC)
3

Forced expiratory volume (FEV)
4

Residual volume (RV)
5

Slow vital capacity (SVC)

6

Forced expiratory flow 25% to 75%
7

Functional residual capacity (FRC)
8

Maximum voluntary ventilation (MVV)
9

Peak expiratory flow (PEF).
10

Total lung capacity (TLC)

What Abnormal Results Mean?
Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) may yield abnormal results for various reasons, indicating potential issues with lung function. Here are some common abnormalities that might be detected in PFTs:
Other lung diseases make the lungs scarred and smaller so that they contain too little air and are poor at transferring oxygen into the blood. These lung diseases are called as restrictive lung diseases.
1

Extreme overweight
2

Lung cancer

3

Fibrosis of the lungs
4

Sarcoidosis and scleroderma

Risks
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is generally considered a safe procedure, but like any medical test, it does carry some risks, though they are minimal for most people. Here are a few potential risks associated with PFT: Discomfort,Coughing and Wheezing,Dizziness
Considerations
Pulmonary function testing results are effort-dependent. It makes patient cooperation crucial while performing the test. It’s difficult to perform in small children and must be avoided in patients suffering from severe lung disease. Lying down is a preferred position in obese patients.
Absolute contraindication
Cardiac surgery/Myocardial Infarction in the past 1 month
Recent thoracic/abdominal/eye surgery in the past 1 month
History of pulmonary embolism
History of aneurysms abdominal/thoracic/ cerebral
Presence of facial palsy/contractures
Patient unwilling to perform the test.
Activities that should be avoided before Pulmonary function testing
Smoking tobacco in any form in the last 2-4 hrs
Consuming tea/coffee/caffeinated drinks in the past 6 hr
Heavy meal in past 4 to 5 hour
Heavy exercise in the past ½ hour
Bronchodilators: inhaled/oral
Alcohol
Lower respiratory tract infection in the past 15 days
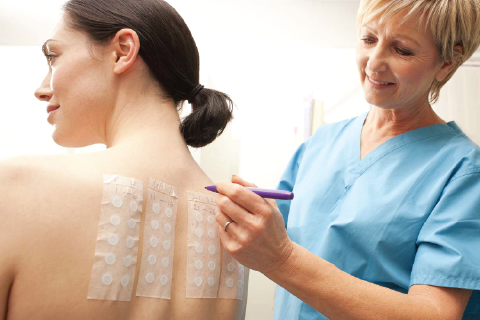


PATCH TESTING
Patch testing is a method used to diagnose allergic reactions to cosmetics, fragrances, and other products that come into contact with the skin
Here’s how it works:
A small amount of the substance being tested is placed onto a small patch of hypoallergenic tape or adhesive.
The patch is then applied to a healthy area of skin, usually the upper back.
The patch is left in place for 48 hours.
After 48 hours, the patch is removed, and the skin is examined for signs of inflammation, such as redness, swelling, and itching.
Results are typically read at 48 and 96 hours after patch removal.
If there is a positive reaction, meaning the skin develops a rash or other symptoms of an allergic reaction, the substance being tested is likely the cause.
Patch testing should always be done by a healthcare professional, typically an allergist or dermatologist, who can interpret the results and recommend appropriate treatment if necessary
- Common Allergens Tested–Includes metals (e.g., nickel), rubber, leather, formaldehyde, lanolin, fragrances, toiletries, hair dyes, medicines, and food additives.
You may advise a patch test
If you suspect cosmetic substance and hair dye as a cause of your inflamed, red, dry and itchy skin.
If you have a dermatitis that is resistant to the treatment, Please ensure that you are not allergic to the ingredients of the cream/lotion prescribed by your dermatologist.
Work-related dermatitis/ occupational dermatitis
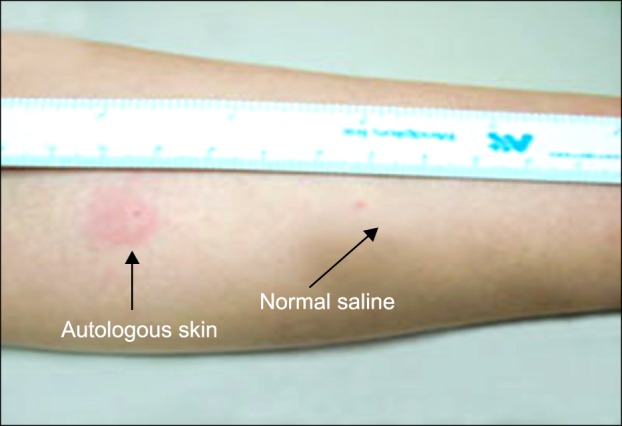
AUTOLOGOUS SERUM SKIN TEST
Autologous serum skin test, also known ASST, is a diagnostic procedure used in identifyin autoimmune urticaria, a condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, resulting in hives or welts on the skin.
Here’s how the test typically works:
Blood Sample Collection: A small sample of the patient’s blood is drawn.
Serum Extraction: The blood sample is then processed to extract the serum, which is the liquid part of blood that remains after clotting and blood cells have been removed.
Injection: A diluted solution containing the patient’s own serum is injected under the skin, usually on the forearm.
Observation: The injection site is monitored for any signs of a reaction, such as redness, swelling, or hives.
Key point about ASST test
It is considered positive if the serum-induced wheal has a diameter at least 1.5 mm greater than the saline control
- Positivity indicates the presence of circulating functional histamine-releasing autoantibodies against IgE or the IgE receptor.
- In chronic spontaneous urticaria, ASST positivity ranges from 30-80%.
- A positive ASST correlates with disease severity, higher total IgE levels, thyroid auto antibodies, and risk of angioedema
- It is a simple, rapid and inexpensive screening test that can help diagnose autoimmune urticaria.
However, the ASST has limitations:
- Sensitivity and specificity are around 70-80%
- False positives can occur due to variations in injection technique
- A negative ASST does not completely rule out autoimmunity
In summary, the ASST is a useful clinical tool to identify autoimmune causes in chronic urticaria, but should be interpreted in conjunction with the patient’s history and other investigation.



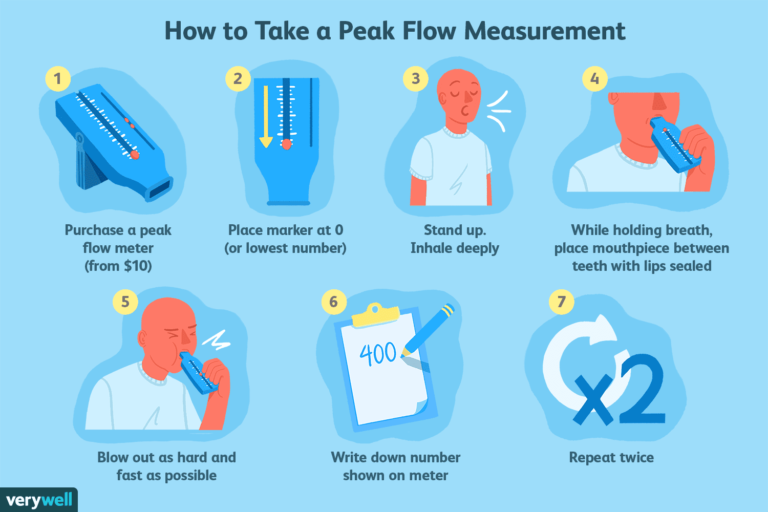
PEAK FLOW MONITORING
Use of Peak flow meter
Green zone
Yellow zone
Red zone
Medical alert Shortness of breath Medicines not working Cannot do usual activity It is an emergency. Call your Doctor.